
How often do researchers look for the right survey respondents, either for a market research study or an existing survey in the field? The sample or the respondents of this research may be selected from a set of customers or users that are known or unknown.
You may often know your typical respondent profile but don’t have access to the respondents to complete your research study. At such times, researchers and research teams reach out to specialized organizations to access their panel of respondents or buy respondents from them to complete research studies and surveys.
These could be general population respondents that match demographic criteria or respondents based on specific criteria. Such respondents are imperative to the success of research studies.
This article discusses in detail the different types of samples, sampling methods, and examples of each. It also mentions the steps to calculate the size, the details of an online sample, and the advantages of using them.
A sample is a smaller set of data that a researcher chooses or selects from a larger population using a pre-defined selection bias method. These elements are known as sample points, sampling units, or observations.
Creating a sample is an efficient method of conducting research . Researching the whole population is often impossible, costly, and time-consuming. Hence, examining the sample provides insights the researcher can apply to the entire population.
For example, if a cell phone manufacturer wants to conduct a feature research study among students in US Universities. An in-depth research study must be conducted if the researcher is looking for features that the students use, features they would like to see, and the price they are willing to pay.
This step is imperative to understand the features that need development, the features that require an upgrade, the device’s pricing, and the go-to-market strategy.
In 2016/17 alone, there were 24.7 million students enrolled in universities across the US. It is impossible to research all these students; the time spent would make the new device redundant, and the money spent on development would render the study useless.
Creating a sample of universities by geographical location and further creating a sample of these students from these universities provides a large enough number of students for research.
Typically, the population for market research is enormous. Making an enumeration of the whole population is practically impossible. The sample usually represents a manageable size of this population. Researchers then collect data from these samples through surveys, polls, and questionnaires and extrapolate this data analysis to the broader community.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
The process of deriving a sample is called a sampling method. Sampling forms an integral part of the research design as this method derives the quantitative and qualitative data that can be collected as part of a research study. Sampling methods are characterized into two distinct approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling is a method of deriving a sample where the objects are selected from a population-based on probability theory. This method includes everyone in the population, and everyone has an equal chance of being selected. Hence, there is no bias whatsoever in this type of sample.
Each person in the population can subsequently be a part of the research. The selection criteria are decided at the outset of the market research study and form an important component of research.
LEARN ABOUT: Action Research
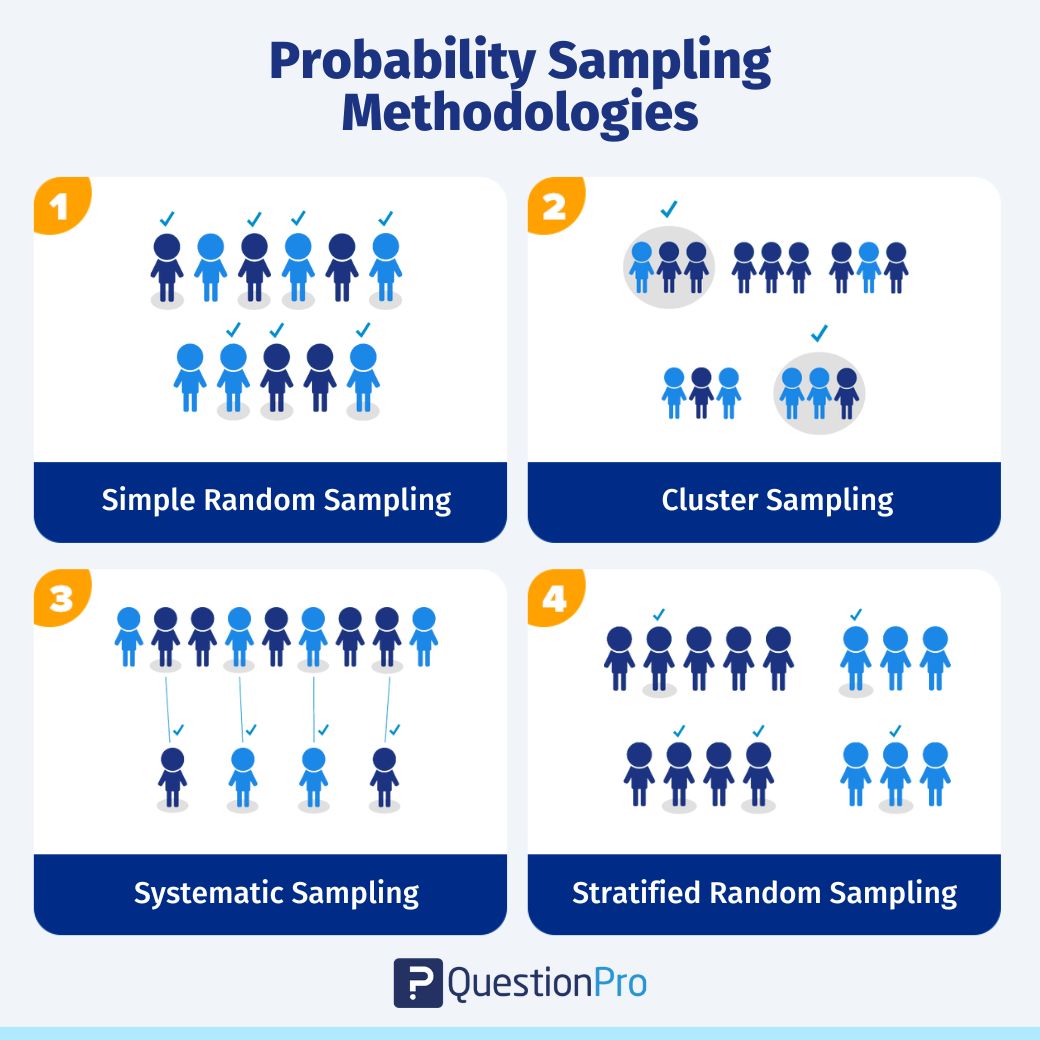
Probability sampling can be further classified into four distinct types of samples. They are:
LEARN ABOUT: Purposive Sampling
The non-probability sampling method uses the researcher’s discretion to select a sample. This type of sample is derived mostly from the researcher’s or statistician’s ability to get to this sample.
This type of sampling is used for preliminary research where the primary objective is to derive a hypothesis about the topic in research. Here each member does not have an equal chance of being a part of the sample population, and those parameters are known only post-selection to the sample.
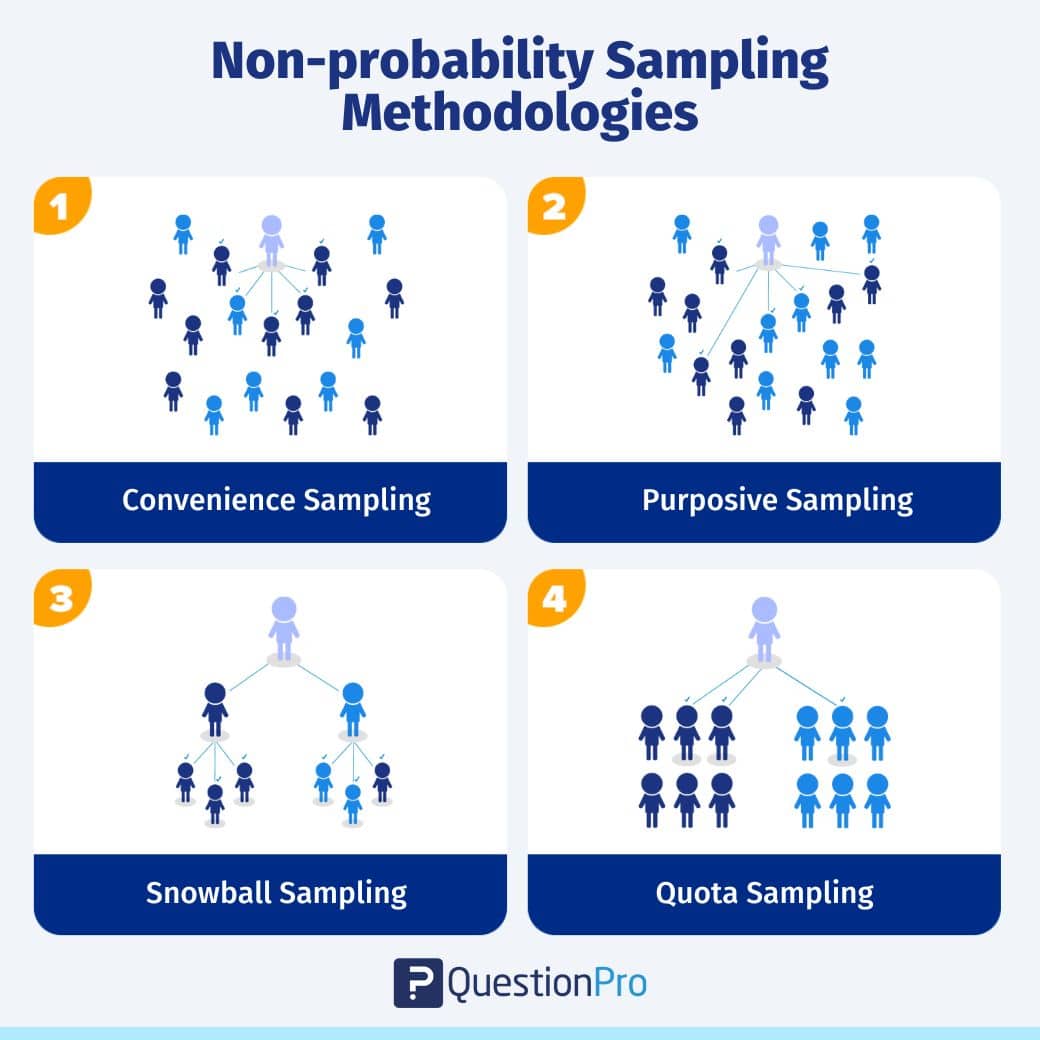
We can classify non-probability sampling into four distinct types of samples. They are:
This non-probability sampling method is used when there is time and costs limitations in collecting feedback. For example, researchers that are conducting a mall-intercept survey to understand the probability of using a fragrance from a perfume manufacturer. In this sampling method, the sample respondents are chosen based on their proximity to the survey desk and willingness to participate in the research.
For example, if the research topic is understanding what University a student prefers for Masters, if the question asked is “Would you like to do your Masters?” anything other than a response, “Yes” to this question, everyone else is excluded from this study.
For example, while collecting feedback about a sensitive topic like AIDS, respondents aren’t forthcoming with information. In this case, the researcher can recruit people with an understanding or knowledge of such people and collect information from them or ask them to collect information.
As we have learned above, the right sample size determination is essential for the success of data collection in a market research study. But is there a correct number for the sample size? What parameters decide the sample size? What are the distribution methods of the survey?
To understand all of this and make an informed calculation of the right sample size, it is first essential to understand four important variables that form the basic characteristics of a sample. They are:
To calculate the sample size, you need the following parameters.
To calculate use the sample size, use this formula:

Sample Size = (Z-score)2 * StdDev*(1-StdDev) / (margin of error)2
Consider the confidence level of 90%, standard deviation of .6 and margin of error, +/-4%
603 respondents are needed and that becomes your sample size.
Try our sample size calculator to give population, margin of error calculator, and confidence level.
As shown above, there are many advantages to sampling. Some of the most significant advantages are:
To collect accurate data for research, filter bad panelists, and eliminate sampling bias by applying different control measures. If you need any help arranging a sample audience for your next market research project, contact us at [email protected]. We have more than 22 million panelists across the world!
In conclusion, a sample is a subset of a population that is used to represent the characteristics of the entire population. Sampling is essential in research and data analysis to make inferences about a population based on a smaller group of individuals. There are different types of sampling, such as probability sampling, non-probability sampling, and others, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Choosing the right sampling method depends on the research question, budget, and resources is important. Furthermore, the sample size plays a crucial role in the accuracy and generalizability of the findings.
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the definition, types, formula, and examples of sampling. By understanding the different types of sampling and the formulas used to calculate sample size, researchers and analysts can make more informed decisions when conducting research and data unit of analysis.
Sampling is an important tool that enables researchers to make inferences about a population based on a smaller group of individuals. With the right sampling method and sample size, researchers can ensure that their findings are accurate and generalizable to the population.
Utilize one of QuestionPro’s many survey questionnaire samples to help you complete your survey.
When creating online surveys for your customers, employees, or students, one of the biggest mistakes you can make is asking the wrong questions. Different businesses and organizations have different needs required for their surveys.
If you ask irrelevant questions to participants, they’re more likely to drop out before completing the survey. A questionnaire sample template will help set you up for a successful survey.